Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security system that demands more than just a single password to let you in. To access an application, an online account, or any other resource, users have to provide two or more separate pieces of evidence—or "factors"—to prove they are who they say they are. It’s a foundational layer of defense that keeps your accounts safe even if one factor, like your password, gets stolen.
Beyond The Password A Simple Guide To Layered Security

Imagine your business data is locked away inside a high-security vault. Your password is the first key, but what happens if a thief manages to get their hands on it? If you only have one lock, they have instant access to everything inside.
This is where multi-factor authentication comes in. It adds a second, and sometimes even a third, lock to that vault door.
Now, even if a cybercriminal has your stolen key (the password), they're stopped dead in their tracks. They can't get past the next lock because they don't have the other required credentials. This layered approach is the simple but powerful idea behind MFA. It’s not just a nice-to-have, either; research from Microsoft shows that MFA can block over 99.2% of account compromise attacks, making it one of the single most effective security tools you can deploy.
The Three Pillars Of Verification
At its core, MFA works by asking you to prove your identity using different kinds of evidence. To grant access, a true MFA system requires you to provide proof from at least two of these three distinct categories.
This structure is what makes it so robust. Let's break down the three core pillars of authentication factors.
| Factor Type | Description | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Something You Know | Secret information that only the user should possess. This is the most common factor. | Password, PIN, Security question answers |
| Something You Have | A physical object or device in the user's possession. | Smartphone (for push notifications/codes), Hardware security key (YubiKey), Smart card |
| Something You Are | Unique biological traits of the user, also known as biometrics. | Fingerprint scan, Facial recognition, Voiceprint analysis |
By combining factors from these different groups—like a password (knowledge) and a fingerprint scan (inherence)—you create a much more formidable barrier. A hacker might be able to phish your password, but they can't easily steal your fingerprint from across the globe.
This multi-layered defense is more important than ever. Stolen credentials are a top cause of data breaches, with some industry reports indicating their involvement in as many as 49% of all breaches. This statistic alone shows just how fragile password-only protection really is.
Ultimately, MFA shifts your security from a single point of failure to a resilient, multi-layered system. It ensures that even if one layer is compromised, other checks are in place to safeguard your company’s assets, your clients’ sensitive data, and your hard-earned reputation.
How Multi-Factor Authentication Actually Works
Let's break down what actually happens when you log in using MFA. Think of it less like a single password and more like a sequence of security checkpoints. It's a quick process for you, but a dead end for anyone trying to impersonate you.
The whole thing starts the moment you type in your username and password. This is your first layer of security—the knowledge factor, or "something you know." The system immediately checks if that password matches what it has on file for your account. If it's wrong, the process stops right there.
But if the password is correct, the security check is far from over. This is the exact moment MFA steps in and proves its worth over old-fashioned, password-only logins.
The Second Security Checkpoint
Instead of just letting you in, the system now asks for a second piece of proof from a completely different category. This is the "multi-factor" part in action. It’s a live, real-time demand for evidence that you are who you say you are, not just someone who found a password scribbled on a sticky note.
This second request can come in a few common forms, depending on how everything is set up:
- A Push Notification: A message pops up on an app on your smartphone, asking you to simply tap "Approve" or "Deny" for the login attempt.
- A One-Time Passcode (OTP): You'll get a unique, short-lived code, usually from an authenticator app like Google Authenticator or sent as a text message. You have to enter this code to move forward.
- A Biometric Scan: You might be asked to scan your fingerprint or use your device's facial recognition to prove it's really you.
Once you provide this second factor and the system confirms it's correct, you're in. It’s only after both your password and your second credential have been verified that the system grants you access.
The beauty of this process is that it creates a powerful security gate. Even if a cybercriminal steals your password from a data breach or a phishing email, that one piece of information is now completely useless on its own. They are stopped cold at the second step without your physical device or your fingerprint.
The Attacker's Roadblock
Picture a hacker who just bought your password on the dark web. They go to your login page, enter it correctly, and feel confident. But then, the system asks for a code that was just sent to your phone. The attacker doesn't have your phone. They can't get the code, they can't approve the notification. Their attempt is dead in the water, and your account stays safe.
That is the simple but incredibly powerful advantage of MFA. It makes stolen passwords almost worthless by demanding a second, separate proof of identity that an attacker can't easily fake or steal. To get a better sense of how one of these factors is put into practice, you can explore how businesses use reliable SMS verification services to secure access.
By adding one tiny, extra step to your login, you put a massive barrier between your critical data and the people trying to steal it. You’ve just turned a single, fragile lock into a multi-layered security system.
Understanding Your Authentication Factor Options
When it comes to setting up multi-factor authentication, it’s not just about adding more steps; it’s about adding the right kind of steps. Think of it like a home security system: a deadbolt and a window lock are good, but a deadbolt, a window lock, and a motion sensor are much better. The strength of your MFA setup comes from combining different types of proof.
These different types of proof, or "factors," fall into three main categories. Each one represents a unique way to confirm you are who you say you are.
For your MFA to be truly effective, you need to pull from at least two of these categories. Stacking two factors from the same group—like a password and a security question—is like having two locks on the same door. It's better than one, but a thief who can pick one can probably pick the other. A password plus a fingerprint scan is a whole different ballgame.
This flow chart gives a great visual of how this works in practice. It's a simple, powerful checkpoint.
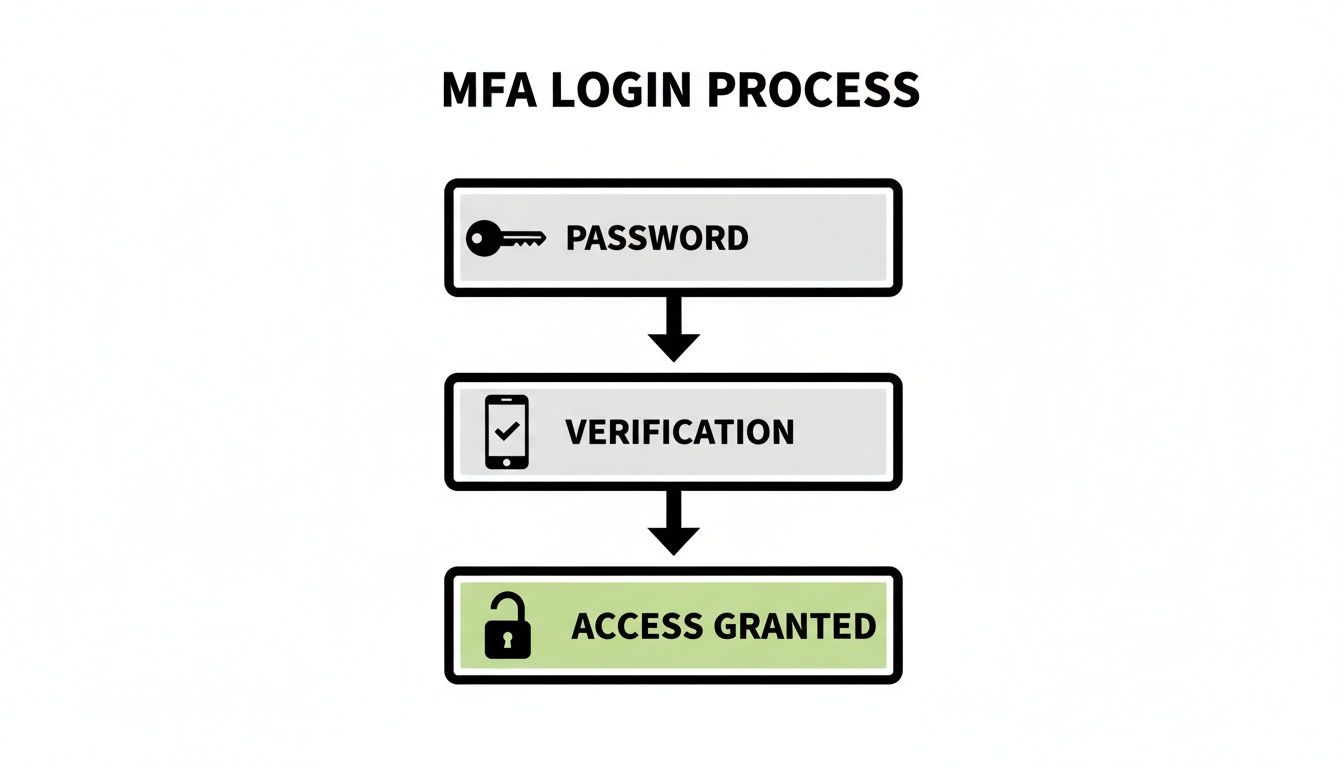
As you can see, that verification step is the critical barrier that stops an intruder, even if they've managed to steal your password.
The Knowledge Factor: Something You Know
This is the one we're all familiar with. A knowledge factor is some piece of secret information that, theoretically, only you have memorized. It’s the old-school gatekeeper of the digital world.
- Passwords: The classic, but also the most vulnerable to being stolen in data breaches or tricked out of you through phishing scams.
- PINs (Personal Identification Numbers): Basically a short, numeric password. They're easier to remember but also easier for a brute-force attack to crack.
- Security Questions: Questions like "What was your first pet's name?" are a weak link. The answers are often easy to guess or can be dug up from social media profiles.
Knowledge factors are a necessary first layer, but relying on them alone is asking for trouble. Their biggest flaw? They can be stolen or guessed, and you might not even know it's happened.
The Possession Factor: Something You Have
This is where security gets a lot more tangible. A possession factor requires you to have a physical device or a specific digital token to prove you're you. This is a game-changer because a hacker can't just steal it from a database—they'd have to physically get their hands on your stuff.
- Authenticator Apps: These are mobile apps, like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, that generate a temporary six-digit code that expires every 30-60 seconds.
- Hardware Tokens: These are small, physical devices that look like a keychain fob or a tiny USB stick (like a YubiKey). You either press a button on it to get a code or plug it in to prove you're there.
- SMS Text Codes: This is when a code gets texted to your phone. It's definitely better than nothing, but it's the weakest of the possession factors due to a sneaky attack called "SIM swapping," where a criminal tricks your cell provider into transferring your number to their phone.
To learn more about how these stack up, you can read our guide on what is two-factor authentication. Possession factors are incredibly effective because they tie your identity to something you physically control.
We see MFA adoption varying quite a bit across different fields. The tech industry, for instance, is way out front with an 87% MFA adoption rate, and professional services aren't far behind at 75%. What's really telling, though, is how people prefer to do it. A global survey found that a massive 95% of employees prefer software-based MFA (like authenticator apps), with very few choosing hardware tokens or biometrics.
The Inherence Factor: Something You Are
This is the most personal and, in many ways, the most futuristic category. Also known as biometrics, inherence factors use your unique physical traits for verification. They’re incredibly hard to fake because, well, they're part of you.
- Fingerprint Scans: Now standard on most phones and many laptops, it's fast, convenient, and very secure.
- Facial Recognition: Think of Apple's Face ID or Windows Hello. These systems use a detailed map of your facial structure to grant access.
- Voice Recognition: Some services can identify you just by the unique sound and cadence of your voice.
What makes inherence factors so great is that they're almost completely frictionless. You don't have to remember a password or dig a token out of your pocket. For a law firm or a medical office handling highly sensitive information, pairing a strong password (knowledge) with a quick fingerprint scan (inherence) creates a powerful security shield that's also incredibly easy for your team to use every day.
Why Your Small Business Needs MFA Right Now
For a small or mid-sized business, a single security breach isn't just an IT headache. It can be a company-ending event. It’s time to move past the what of multi-factor authentication and talk about why it's one of the most urgent and critical investments you can make for your business's survival.
Think about it—the internet is flooded with automated bots constantly rattling digital doorknobs, testing for a weak password. A password alone is like leaving your front door locked with a cheap lock that anyone can pick. MFA is the deadbolt and security chain; it stops intruders cold, even if they somehow got a copy of your key.
This isn't just about protecting your own files. It's about protecting your clients, your reputation, your finances, and your future.
Shielding Your Business From Cyber Attacks
Most cybercriminals aren't masterminds; they're opportunists using the same old tricks because, far too often, they still work. They count on small businesses sticking with outdated password-only security. By simply turning on MFA, you shut down their most common and devastating lines of attack.
A stolen password is a thief's golden ticket. Without MFA, they can walk right in. With MFA, they're stopped at the door because they can't provide that second piece of proof.
The infamous 2021 Colonial Pipeline hack that crippled fuel supply chains started with a single compromised password found on the dark web. It’s a powerful lesson: password-only systems are a massive liability. MFA makes a stolen password practically useless by itself.
It's no surprise that MFA adoption is skyrocketing. One recent study found that 57% of businesses are now using it. The global MFA market has exploded to USD 16.3 billion and is projected to hit a staggering USD 70 billion by 2033. This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift in how businesses protect themselves.
Implementing MFA is a foundational step in building a strong identity security posture management strategy. It's one of the single most effective ways to protect user accounts and the sensitive data behind them.
The table below breaks down some of the most common threats your business faces and shows exactly how MFA acts as your first and best line of defense.
Top Cyber Threats Mitigated by MFA
| Cyber Threat | How It Works | How MFA Protects Your Business |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Scammers send deceptive emails to trick employees into revealing their passwords on a fake login page. | Even if an employee gives away their password, the attacker can't log in because they don't have the second factor (e.g., the employee's phone). |
| Credential Stuffing | Attackers use lists of stolen usernames and passwords from other breaches to try logging into your systems, hoping people reuse passwords. | MFA blocks these attempts completely. The attacker has the password but lacks the required second factor, rendering the stolen credentials useless. |
| Brute-Force Attacks | Automated software tries thousands of password combinations per second to guess an employee's password. | While a strong password policy helps, MFA makes brute-force attacks impractical. The attacker would also need to guess or steal the second factor. |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks | A hacker intercepts communication between a user and a service to steal credentials as they are entered. | Advanced MFA methods (like FIDO2) are resistant to MitM attacks, but even basic MFA makes it significantly harder for the attacker to succeed. |
Simply put, MFA neutralizes the most common ways cybercriminals get in, giving you a massive security upgrade for a relatively small investment.
Protecting Client Trust and Meeting Compliance
If you run a law firm, dental practice, or any professional service, your entire business is built on a foundation of trust. A data breach that exposes sensitive client or patient information can destroy that trust overnight, leading to lost clients, lawsuits, and a damaged reputation that's hard to repair.
MFA is a tangible, visible way to show your clients and partners that you take their privacy seriously.
On top of that, many industries have strict data protection rules you simply can't ignore. For example:
- HIPAA: This health information act requires strong safeguards for patient data, making MFA a non-negotiable for healthcare providers.
- PCI-DSS: If you process credit cards, this standard mandates MFA for anyone accessing the cardholder data environment.
- State-Level Privacy Laws: A growing number of states require businesses to implement "reasonable security measures," and MFA is now widely considered a baseline standard.
Ignoring these regulations can lead to crippling fines and legal battles. MFA isn't just a good idea; in many cases, it's the law.
Locking down your access points is also vital for keeping your business running smoothly. You can learn more in our guide on how to secure remote access. By preventing security incidents, you avoid the operational chaos that grinds a business to a halt. It’s a small step that delivers a huge return in security and peace of mind.
How We Put MFA to Work for Your Business

Knowing you need multi-factor authentication is one thing. Actually rolling it out without causing a massive headache for your team is another challenge entirely. This is where theory hits the pavement, and it's where our experience at GT Computing makes all the difference.
We specialize in making robust security feel simple for small businesses. Our goal is to weave MFA into your daily workflow so smoothly that it protects your team without ever getting in their way. You get to focus on your business, knowing your digital front door is locked tight, and we handle the technical heavy lifting.
After years of helping businesses across Connecticut protect their data, we know that there's no such thing as a one-size-fits-all security plan. Your business has its own unique software, workflows, and risks, and your MFA strategy needs to reflect that.
Your Path to Stronger Security
We’ve refined our process to ensure every MFA rollout is seamless and effective. It all starts with a conversation to understand your specific environment and goals, making sure the final setup is a perfect fit for how you operate.
Here’s a look at our strategic approach:
Comprehensive Security Assessment: First, we take a deep dive into your current IT setup. We map out every access point to your network and data—from cloud apps like Microsoft 365 to your VPN and other critical software. This helps us pinpoint your vulnerabilities and prioritize what needs to be locked down first.
Strategic Solution Design: With a clear picture of your needs, we design a custom MFA strategy. We’ll help you choose the right authentication factors, balancing the rock-solid security of a physical token with the sheer convenience of a push notification. The key is finding a solution that integrates perfectly with the tools you already use.
Seamless Deployment and Configuration: Our certified technicians handle the entire implementation from start to finish. We configure smart MFA policies that align with your workflow—for example, we might require re-authentication from a new device or location but not every time an employee signs in from the office. This keeps security high and frustration low.
Team Training and Onboarding: Great technology is useless if your team doesn’t know how to use it. We provide clear, simple training for your staff, walking them through exactly how the new process works. Our hands-on approach takes the mystery out of MFA, ensures everyone is on board, and turns your team into your greatest security asset.
A common fear we hear from business owners is that new security will just frustrate employees and kill productivity. We’ve designed our entire process to avoid that. By picking user-friendly methods and setting up intelligent policies, we make security a quick, background habit instead of a daily annoyance.
Ongoing Management and Support
Our job isn’t done once MFA is up and running. Good security is a process, not a project. As part of our complete managed IT services for small business, we stick around to provide continuous monitoring and support.
This proactive management includes:
- Watching for suspicious login attempts and quickly responding to potential threats.
- Managing user access as your team evolves, securely adding new hires and removing access for those who have left.
- Keeping your security systems updated to shield you from the latest threats.
- Providing a responsive help desk for any questions or issues your team runs into.
With GT Computing, implementing MFA is about more than just checking a box. It’s about building a resilient, long-term defense that protects your client data, secures your finances, and preserves the reputation you've worked so hard to build. We’ll handle the IT, so you can handle your business.
Ready to Lock Down Your Business?
Putting robust security like MFA in place shouldn't be a headache. At GT Computing, we take the complexity out of IT, providing fast, reliable support that lets you focus on what you do best: running your business.
Whether you're looking to implement MFA, manage your network, or need a trusted partner for all your IT needs, we're here to help you stay secure and productive.
Let's talk about your security.
Call us at 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com for a free, no-obligation consultation today.
Your MFA Questions, Answered
When you're thinking about adding a new security layer like multi-factor authentication, it’s natural to have questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones we hear from business owners so you can feel confident about making the switch.
Isn't This Going to Be Expensive for a Small Business?
Not at all. In fact, you might be surprised to learn that many of the tools you're already paying for, like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, come with powerful MFA features built right in. The trick is just making sure they're turned on and set up properly to give you real protection.
Think of it this way: the small investment in time to get MFA configured is nothing compared to the massive financial hit and reputation damage that comes from a data breach. We focus on using the tools you have or finding other budget-friendly options that work for you.
Will This Annoy My Team and Slow Us Down?
When implemented thoughtfully, MFA is just a quick, minor step that quickly becomes a habit. Most modern solutions are designed to be user-friendly, often requiring nothing more than a quick tap on a smartphone app.
We can also set up smart policies that only ask for that extra verification step when it makes sense—like when someone tries to log in from a new device or an unfamiliar network. This strikes the perfect balance between security and convenience, keeping your team productive without sacrificing protection.
Can We Even Use This With Our Current Software?
Almost certainly, yes. Most modern cloud-based software, VPNs for remote work, and email systems are designed to work perfectly with MFA. As part of our process, we'll take a look at your entire tech setup to make sure the rollout is seamless. From your main email platform to that specialized industry software you rely on, we can create a consistent security shield across all your important tools.
What's the Real Difference Between MFA and 2FA?
This one's simple. Think of MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) as the umbrella term for any system that requires more than one piece of proof to log in.
2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) is just a specific, very common type of MFA. As its name suggests, it always uses exactly two factors. While 2FA is a huge security upgrade for most businesses, some highly sensitive systems might even require three factors (like a password + a physical key + a fingerprint scan).
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com



