Before you even think about buying new equipment, let's cover a few quick changes that can make a world of difference. Frustratingly slow downloads, video calls that constantly buffer, and those annoying dead zones in your office are often symptoms of simple problems that, thankfully, have easy solutions.
The goal here is to knock out the most common culprits first. These are the tricks of the trade that often give you an immediate performance boost without needing a technical degree.
Quick Fixes for a Stronger WiFi Signal Now

Sometimes the most frustrating tech issues have the simplest fixes. Before you go down a rabbit hole of complex diagnostics, running through these initial steps can often resolve the majority of common WiFi headaches. I've seen these simple tweaks solve major connectivity problems for businesses more times than I can count.
If you're dealing with a specific issue, this table can help you pinpoint the likely cause and the first thing you should try.
Common WiFi Problems and Their Quick Solutions
| Symptom | Potential Cause | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|
| No Internet Connection | Router or Modem Overload | Power cycle both your modem and router (the classic reboot). |
| Slow Speeds Everywhere | Outdated Firmware | Log in to your router's admin panel and check for a firmware update. |
| Weak Signal in Certain Rooms | Poor Router Placement | Move your router to a central, elevated location away from walls. |
| Random Connection Drops | Channel Interference | Change your WiFi channel to a less congested one (e.g., 1, 6, or 11 for 2.4 GHz). |
These quick actions are your first line of defense and can often get your network back up to speed in minutes.
Rethink Your Router Placement
Where you put your router is, without a doubt, the single biggest factor in your signal strength. WiFi signals are just radio waves, and they get weaker as they travel and really struggle to push through certain materials. Sticking your router in the most central location in your home or office is the best way to get balanced coverage.
But "central" isn't just about left and right; it's also about up and down.
- Go high. Placing your router on a top shelf or mounting it on a wall is a game-changer. Radio waves travel downwards and outwards, so elevating it helps the signal reach both the first and second floors much more effectively.
- Avoid the kitchen. Microwaves are notorious signal killers because they operate on a similar 2.4 GHz frequency. Running the microwave can temporarily knock nearby devices right off your network.
- Stay away from dense materials. This is a big one. Concrete, brick, and metal are WiFi’s worst enemies. A router tucked away in a basement behind concrete walls will barely be able to send a usable signal to the rest of the building.
Even things you might not suspect can cause issues. I've seen large aquariums (water absorbs radio waves) and metal filing cabinets create unexpected dead zones that kill productivity.
The Power of a Proper Reboot
I know, "Have you tried turning it off and on again?" sounds like a cliché, but it's a vital maintenance step for a reason. Over time, your router’s memory gets bogged down with temporary data, which leads to sluggish performance and random connection drops. A reboot clears out all that junk and gives it a fresh start.
Simply pulling the power cord out and plugging it right back in isn't going to cut it. For a true reset, you have to give the internal components a moment to fully discharge.
The right way to do it is to unplug both your router and your modem from the power outlet. Just let them sit for at least 30-60 seconds. Then, plug the modem back in first and wait for all its lights to become stable. Once it's fully online, you can plug the router back in and give it a few minutes to boot up. For a business, doing this weekly can prevent a lot of performance headaches down the road.
Keep Your Firmware Updated
Firmware is the software that runs on your router, telling it how to operate. Manufacturers are always releasing updates to patch security holes, fix bugs, and, most importantly, improve performance. These updates can directly boost your signal strength and stability.
Running on outdated firmware is like driving a car that’s never had an oil change. It not only leaves your network wide open to security threats but also means you’re missing out on key optimizations. Most modern routers have an "auto-update" feature buried in their settings—turning it on is one of the smartest, simplest things you can do for your network. If yours doesn't, get in the habit of logging into your router's admin panel every few months to check manually. It’s a five-minute task that keeps your hardware running as efficiently and securely as possible.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com
Pinpointing Your WiFi Signal Weaknesses

Alright, you've tried the quick fixes. Now it’s time to stop guessing and start measuring. If you want to permanently solve those frustrating connection drops and actually improve your WiFi signal, you need to know what you're up against. This means looking past the simple signal bars on your phone and digging into the real data.
Don't worry, this is less technical than it sounds. It’s about using some simple, often free, tools to see exactly where your network is struggling and, more importantly, why. Armed with that knowledge, you can make targeted changes that work, instead of just shuffling the router around and hoping for the best.
What Do Those WiFi Bars Actually Mean?
When your laptop shows you three out of four WiFi bars, what is it really telling you? That's a simplified visual, but behind it are specific metrics that paint the true picture of your connection quality. Learning to read these numbers is the first step to becoming your own network detective.
The industry standard for measuring WiFi signal is in decibels relative to 1 milliwatt (dBm), often shown as a negative number. This value is sometimes referred to as the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). The scale might seem backward at first: a number closer to zero is better.
A signal typically ranges from -30 dBm (the best you'll ever see) down to -90 dBm (basically unusable). For demanding tasks like video calls or streaming, you really want to be in the -55 dBm to -70 dBm range. Once you dip below -80 dBm, you'll start experiencing unreliable connections and frustrating drops. If you want to get really granular, TechGrid.com has a great deep dive into WiFi metrics.
This changes everything. Suddenly, you don't just have "bad WiFi" in the conference room; you have a -82 dBm signal that’s too weak to sustain a video call. Now you have a problem you can actually solve.
How to Find Your Signal Strength
You don't need a truck full of expensive gear for this part. Most of your devices have built-in tools or can run free apps that show you this crucial data. This lets you walk around your office or home and get real-time feedback on your signal quality.
Here’s a quick rundown on how to check the dBm on your devices:
- On a Mac: This is the easiest. Just hold down the Option key and click the WiFi icon in your menu bar. You'll see a detailed list, including your current RSSI value.
- On Windows: You'll need a little help from a third-party app. Programs like WiFi Analyzer from the Microsoft Store do a great job of showing signal strength in dBm along with other useful info.
- On Android: Most Android phones show this info natively. You can usually find your signal strength in dBm under your WiFi network's settings. For a more visual approach, an app like WiFi Analyzer works great here too.
- On an iPhone: Apple locks this down a bit, but you can use their own AirPort Utility app. After installing it, go to your iPhone's Settings, find the AirPort Utility section, and toggle on the "Wi-Fi Scanner."
The goal here is to establish a baseline. Walk from room to room and jot down the dBm reading. This will give you a mental map of your strong and weak zones, which is the perfect foundation for the next step.
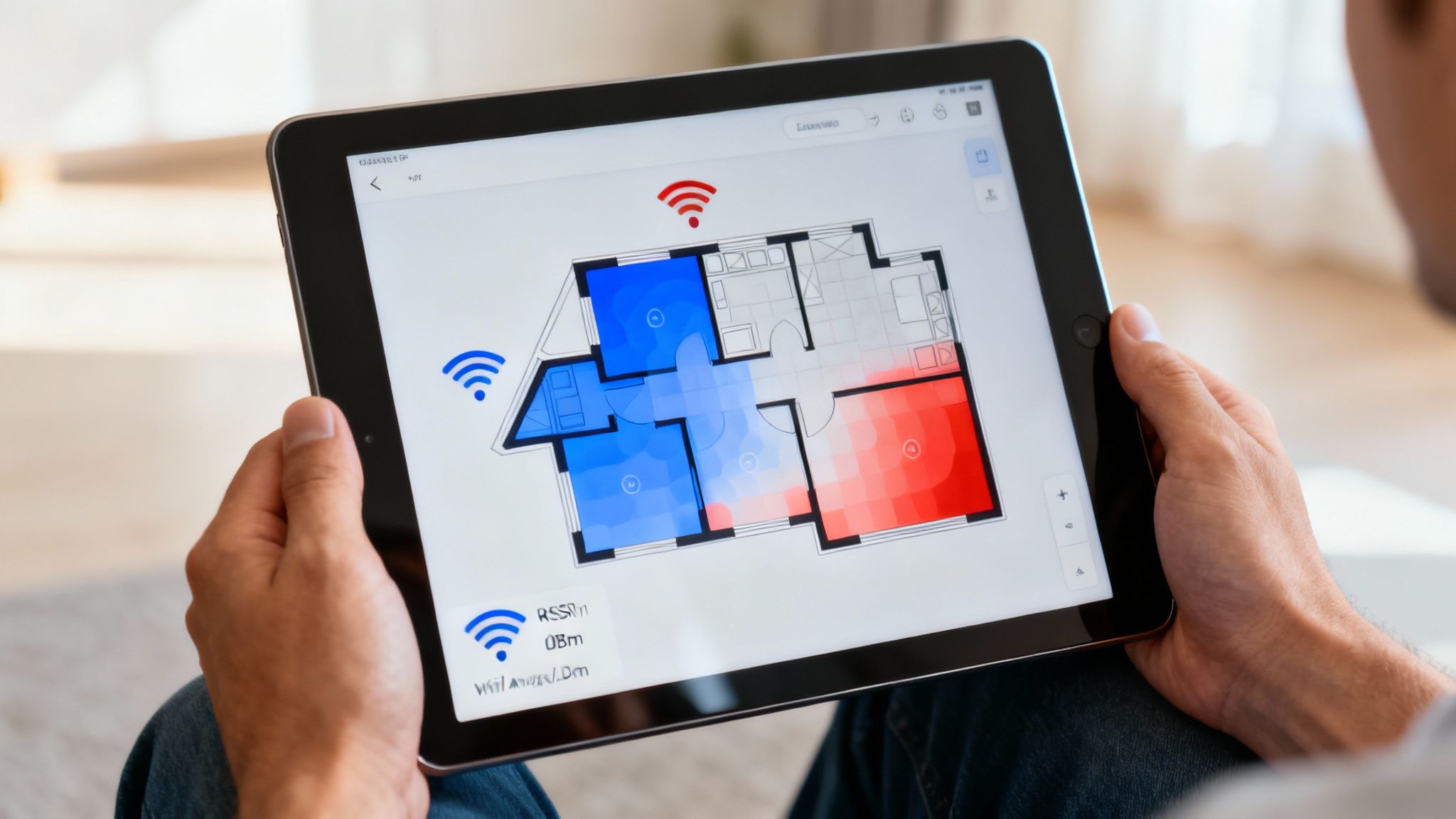
Create a Visual WiFi Heat Map
This is where it all comes together. A WiFi heat map is a visual representation of your signal strength laid over a floor plan of your space. It turns all those abstract dBm numbers into a simple, color-coded map that instantly shows you where your signal is great (green), just okay (yellow), and terrible (red). This is, without a doubt, the most powerful tool for diagnosing WiFi issues.

Tools like NetSpot (which offers a great free version) make this surprisingly easy. You upload a simple floor plan—even a quick sketch will do—and then walk around your space with your laptop. The software tracks your location and measures the signal strength at each point.
In minutes, you'll have a map that clearly reveals:
- Hidden Dead Zones: Those annoying spots where the WiFi just vanishes.
- Interference Sources: You'll see the signal plummet near a microwave or a thick concrete wall.
- Real-World Coverage Gaps: See exactly where your signal starts to fade and becomes unreliable.
With a heat map, you're not flying blind anymore. You can see precisely how moving a router to a more central location would improve coverage, or pinpoint the exact spot where a new access point would do the most good. This is how the pros design reliable networks—with data, not guesswork.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com
Fine-Tuning Your Router Settings for Peak Performance
Your router’s software is a powerful tool for boosting your WiFi signal, but most people never venture beyond the factory defaults. Those out-of-the-box settings are built for universal compatibility, not for the unique layout of your specific office or home. With just a few strategic tweaks, you can often unlock a surprisingly significant performance gain.
Think of your router's admin panel as the control center for your network. Getting in there is the first step to taking control and optimizing your connection. This is where small changes can make a massive difference in your day-to-day internet experience.
Change Your WiFi Channel to Avoid Traffic Jams
If your business is in a crowded office park or you live in an apartment complex, your WiFi is fighting for airtime with dozens of other networks. All those competing signals create a kind of digital gridlock, slowing everyone down. Your router is probably set to "Auto," and while it tries to pick the least crowded channel, it doesn't always nail it.
Manually selecting a less congested channel is one of the quickest and most effective ways to improve your WiFi signal. Just use one of the WiFi analyzer apps we talked about earlier to get a real-time map of which channels your neighbors are hogging.
- On the 2.4 GHz Band: Stick to channels 1, 6, and 11. These are the only three that don’t overlap, which is a fancy way of saying they won't interfere with each other. Simply pick whichever of these three has the fewest networks on it.
- On the 5 GHz Band: This band is your secret weapon. It offers a lot more channels, so it’s naturally less prone to congestion. You have more breathing room here, so just pick a channel that looks wide open on your analyzer app.
Making this one change can feel like turning off a jam-packed side street and merging onto an open highway.
Strategically Use Both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Bands
Most modern routers are dual-band, broadcasting two separate networks: one on the 2.4 GHz frequency and another on the 5 GHz frequency. Each has its own strengths, and using them properly is the key to a stable, high-performance network.
| Frequency Band | Key Advantage | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz | Longer Range: Better at punching through walls and solid objects. | Smart home devices (thermostats, plugs), devices far from the router. |
| 5 GHz | Faster Speeds: Offers more bandwidth and much less interference. | Laptops, smartphones, streaming devices, gaming consoles. |
Instead of letting all your devices pile onto whichever network they see first, you need to direct traffic. Assign your mission-critical devices—like your work laptop or the smart TV in the conference room—to the faster 5 GHz band. This frees up the 2.4 GHz band for your less-demanding gadgets and helps everything run more smoothly.
A classic mistake is giving both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks the same name (SSID). If you give them distinct names, like "OfficeWiFi-2.4" and "OfficeWiFi-5," you get full control over which device connects to which band.
Prioritize Your Traffic with Quality of Service (QoS)
For any business, not all internet traffic is created equal. A video conference with a major client is infinitely more important than a background software update. This is exactly what Quality of Service (QoS) is for. QoS is a router feature that lets you tell it which devices and applications get first dibs on your bandwidth.
For instance, you can configure QoS to guarantee that your VoIP phone system and platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams always have the pipeline they need. This stops them from stuttering or dropping the second someone else in the office starts downloading a huge file. For maintaining business productivity, it’s an absolute game-changer.
In larger or more complex business environments, a single router just won't cut it. You'll likely need to deploy multiple access points to ensure solid coverage everywhere. Learning how to configure wireless access points properly is a crucial step in building a truly robust, enterprise-grade network that won’t buckle under pressure.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com
Choosing the Right Hardware to Eliminate Dead Zones
So, you’ve moved your router, tweaked every setting you can find, and you’re still staring at a single bar of WiFi in the back office. It’s a common frustration, especially in larger buildings or older homes with signal-blocking walls made of brick, plaster, or concrete. When software adjustments and clever positioning just aren’t cutting it, you’ve likely hit the limits of your current hardware.
Let's be honest: the router your internet service provider (ISP) gave you for "free" is built for average, everyday use. It's rarely powerful enough to provide solid coverage across a multi-story home or a busy office floor. Upgrading your hardware is often the most definitive way to kill those dead zones for good and build a network that can handle today's demands.
This quick decision tree can help you diagnose some common culprits before you spend a dime.
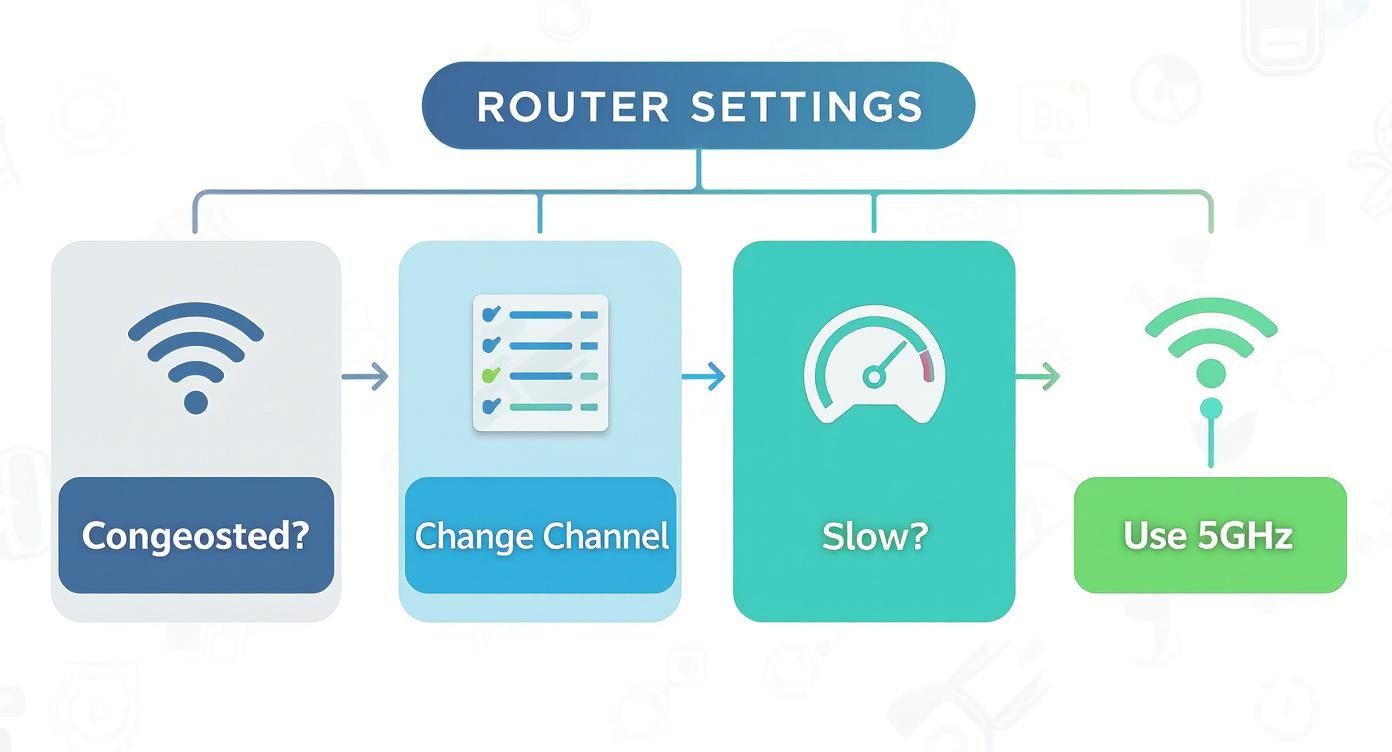
As you can see, sometimes the fix is as simple as switching to a less crowded channel or moving your devices to the 5GHz band. But when it's not, it's time to look at a hardware upgrade.
WiFi Extenders: A Simple, Targeted Fix
The most straightforward hardware solution is a WiFi extender, sometimes called a repeater. The concept couldn't be simpler: you plug it in about halfway between your router and the dead zone. It catches the existing WiFi signal and then rebroadcasts it, pushing the network's edge a little further out.
Think of it as a relay runner in a race, grabbing the signal baton from your router and carrying it further down the track. It's a quick, cost-effective fix if you just have one stubborn dead spot, like a single conference room or a corner bedroom.
But there's a catch. Extenders usually create a separate network (like "OfficeWiFi_EXT"), and your phone or laptop won't automatically hop between them as you move around. More importantly, they typically cut your available bandwidth in half because the same radio has to both receive the signal and then transmit it again.
Powerline Adapters: When Walls Are the Enemy
What if your dead zone is caused by something radio waves just can't muscle through, like a thick concrete wall or an old fireplace? This is where powerline adapters come in. This clever bit of tech uses your building's existing electrical wiring to carry the internet signal.
The setup is a breeze. You plug one adapter into an outlet near your router and connect it via an Ethernet cable. Then, you plug the second adapter into an outlet in the room with the dead zone. Just like that, you've completely bypassed the physical obstruction.
Powerline adapters are a fantastic workaround for architecturally challenging spaces. They essentially turn your electrical system into a high-speed wired network without the mess of running new cables.
This is a go-to solution in older buildings or offices where drilling holes for new Ethernet runs just isn't an option.
Mesh WiFi Systems: The Gold Standard for Seamless Coverage
For total, seamless coverage across a large area, nothing beats a modern mesh WiFi system. A mesh setup replaces your single, lonely router with a team of interconnected "nodes" or "satellites" that you place around your space. These nodes all work together, blanketing the entire area in a single, intelligent network.
Unlike an extender, a mesh system broadcasts one unified network name. As you walk from room to room, your device automatically and seamlessly connects to the strongest node without ever dropping the connection. It’s the definitive way to eliminate dead zones and ensure rock-solid performance everywhere.
The demand for better coverage is driving huge growth, with the global WiFi signal booster market projected to be worth around $8.213 billion by 2025. People are tired of spotty connections. Today's hardware often includes advanced features like MU-MIMO and beamforming, which intelligently direct the WiFi signal toward your devices instead of just broadcasting it in all directions.
When you're trying to cover a business with dozens of devices, VoIP phones, and security cameras, a professional-grade system is the only way to go. To get a better sense of what's out there, you can explore our guide to the best wireless access points for business and see what enterprise-level solutions can do.
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown of how these hardware solutions stack up.
WiFi Hardware Upgrade Comparison
| Hardware Solution | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| WiFi Extender | Fixing a single, isolated dead zone on a budget. | Inexpensive; simple to set up. | Cuts bandwidth by ~50%; creates a separate network; can be unreliable. |
| Powerline Adapter | Bypassing thick walls or floors that block WiFi signals. | Uses existing electrical wiring; provides a stable, wired-like connection. | Performance depends on wiring quality; can be bulky and block outlets. |
| Mesh WiFi System | Large homes or offices needing seamless, whole-area coverage. | One network name; seamless roaming; easy to expand; intelligent traffic management. | More expensive upfront; multiple units to place and power. |
Ultimately, the right hardware depends entirely on your specific problem. An extender can be a perfect quick fix for one room, while a mesh system is a long-term investment for total coverage.
Advanced Network Strategies for Serious Users
https://www.youtube.com/embed/nJ73NFHXJZo
When the usual fixes don't get the job done, it's time to think like a network pro. For businesses, dedicated remote workers, or anyone who can't afford a spotty connection, a standard, off-the-shelf router setup just isn't going to cut it. The strategies here are all about building a network that can handle whatever you throw at it without missing a beat.
This is where we move beyond a single router and start building a genuinely robust, distributed network. The whole point is to push consistent, high-speed WiFi into every corner of your space, stamping out downtime and slowdowns that kill productivity.
The Power of a Wired Ethernet Backhaul
Mesh WiFi systems are great for blanketing a home or office with a signal, but they have a hidden weakness: the connection between the mesh nodes themselves. Most of these systems use a wireless backhaul out of the box, meaning the nodes are all talking to each other over the same WiFi airwaves your laptops and phones are trying to use. It’s convenient, but it’s also a major bottleneck.
If you want to unlock the true potential of your mesh system, you need a wired Ethernet backhaul. This simply means running a physical Ethernet cable from your main router to each satellite node.
- Unleash Maximum Speed: A wired backhaul frees up the entire wireless spectrum for your devices, instead of wasting it on chatter between the nodes.
- Create Unbeatable Reliability: It completely removes the risk of wireless interference between your mesh points, building an incredibly stable foundation for your whole network.
- Get What You Paid For: Your nodes can now deliver the full speed of your internet connection to your devices, not just a fraction of it.
Think of it this way: a wireless backhaul is like having a team of messengers all trying to shout instructions across a crowded, noisy room. A wired backhaul gives each messenger their own private, soundproof tunnel, ensuring every message gets through instantly and perfectly.
Strategic Placement of Multiple Access Points
In larger buildings or offices with tricky layouts, one router—no matter how powerful—is never enough. The professional-grade solution is a system built around multiple Access Points (APs). Unlike a simple repeater or extender, each AP is a dedicated piece of hardware that broadcasts a powerful WiFi signal and is wired directly back to the main network switch.
When you do this right, you create what’s known as distributed WiFi, a strategy designed to blanket an entire property with a seamless, unified signal. It’s a game-changer for challenging environments, and we’ve written a detailed guide on the benefits of a distributed WiFi system that dives deeper into how it solves these problems.
Placement is everything. A professional will perform a site survey, often using a "heat map" tool, to find the exact weak spots and place APs precisely where they’ll have the most impact. This eliminates dead zones and lets your devices roam freely, handing off from one AP to the next so smoothly you'll never even notice it happened.
Future-Proofing with WiFi 6E and WiFi 7
One of the biggest culprits behind a weak WiFi signal is congestion—too many neighboring networks all fighting for the same airwaves. The newest WiFi standards, WiFi 6E and WiFi 7, attack this problem by opening up a brand-new, exclusive fast lane: the 6 GHz band.
This new frequency is like a private, multi-lane superhighway for your data, completely separate from the jam-packed 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands that all your old devices (and your neighbors' devices) are stuck on.
A significant advancement contributing to improved WiFi signal strength and performance is the introduction and spread of the 6 GHz WiFi spectrum. This expanded bandwidth nearly doubles the available WiFi spectrum compared to traditional 5 GHz usage. The cleaner spectrum and wider channels in the 6 GHz band significantly reduce interference and congestion, improving signal quality and speed. Discover more insights about the future of WiFi on OpenSignal.com.
For any business in a crowded office park or a tech-heavy home filled with smart devices, upgrading to WiFi 6E or WiFi 7 hardware is the single best way to sidestep interference. It gives your most important devices a clear, uncontested path to the internet, guaranteeing the fastest possible speeds and lowest latency.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com
Your Top WiFi Boosting Questions, Answered
When you're trying to improve your WiFi, you'll find a lot of advice out there—some good, some… not so good. It’s easy to get lost in the noise. I get asked these questions all the time, so let's clear up a few of the most common ones with practical, no-nonsense answers.
Think of this as your quick-reference guide, based on years of real-world network troubleshooting. We'll bust some myths and talk about what really works.
Can a WiFi Extender Make My Internet Faster?
This is a big one. The short answer is no. A WiFi extender is designed to fix a coverage problem, not a speed problem. Its only job is to grab your existing WiFi signal and push it further, reaching a dead spot in your office or home. It can't magically boost the internet speed coming from your provider.
In reality, most extenders actually cut your potential WiFi speed in half. Why? Because they use the same radio to both talk to the router and talk to your devices, effectively creating a bottleneck. This can reduce your maximum speed by about 50%. If you need both speed and reach in a weak area, a mesh system (especially one with a wired backhaul) or a properly installed access point is a far superior choice.
How Often Should I Update My Router Firmware?
Think of firmware as the operating system for your router. Ignoring updates is a common mistake that leaves your network slow and, worse, vulnerable. I recommend checking for new firmware every month or two. Even better, if your router has an auto-update feature, turn it on and let it do the work for you.
Don't skip these updates! They are critical. Manufacturers release them to patch serious security holes, fix bugs that cause random disconnects, and often include performance tweaks that make your entire network run smoother.
Does Putting Aluminum Foil Behind My Router Actually Work?
Ah, the old foil trick. While there's a tiny bit of science to it—foil can reflect radio waves—it’s a completely unpredictable and clumsy fix. You might accidentally bounce the signal in a weird direction and make things worse in other parts of your building. The results are never consistent.
You'll get a much bigger, more reliable improvement just by moving your router to a central, elevated spot, away from walls and obstructions. For a real, permanent fix to a coverage issue, you're always better off investing in proper hardware like a directional antenna or a modern mesh WiFi system. A piece of kitchen foil just can't compete.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com
Ready to Ditch the IT Headaches for Good?
If you're tired of wrestling with network issues and just want things to work, we're here to help. At GT Computing, we offer practical, reliable support for businesses and home offices alike. From getting a new network off the ground to recovering critical data and managing your day-to-day IT, our goal is to keep you secure, productive, and focused on what you do best.
Let's talk about what you need. Reach out for a straightforward, no-obligation consultation.
You can call us directly at 203-804-3053 or send an email to Dave@gtcomputing.com.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com



