When you're trying to prevent a ransomware attack, you have to think in layers. It's not about one magic tool; it's a combination of smart technology, well-trained people, and a bulletproof backup plan. Building this proactive framework is the only real way to defend against having your business-critical data locked away from you. This isn't just about installing software; it's about fundamentally securing your entire environment from the inside out.
Your Proactive Ransomware Prevention Framework

Let’s get one thing straight: stopping ransomware isn't a product you buy off the shelf. It’s a strategy you build, layer by layer. This framework isn't just theory; it’s a high-level, actionable blueprint designed to make your organization a much tougher nut for attackers to crack.
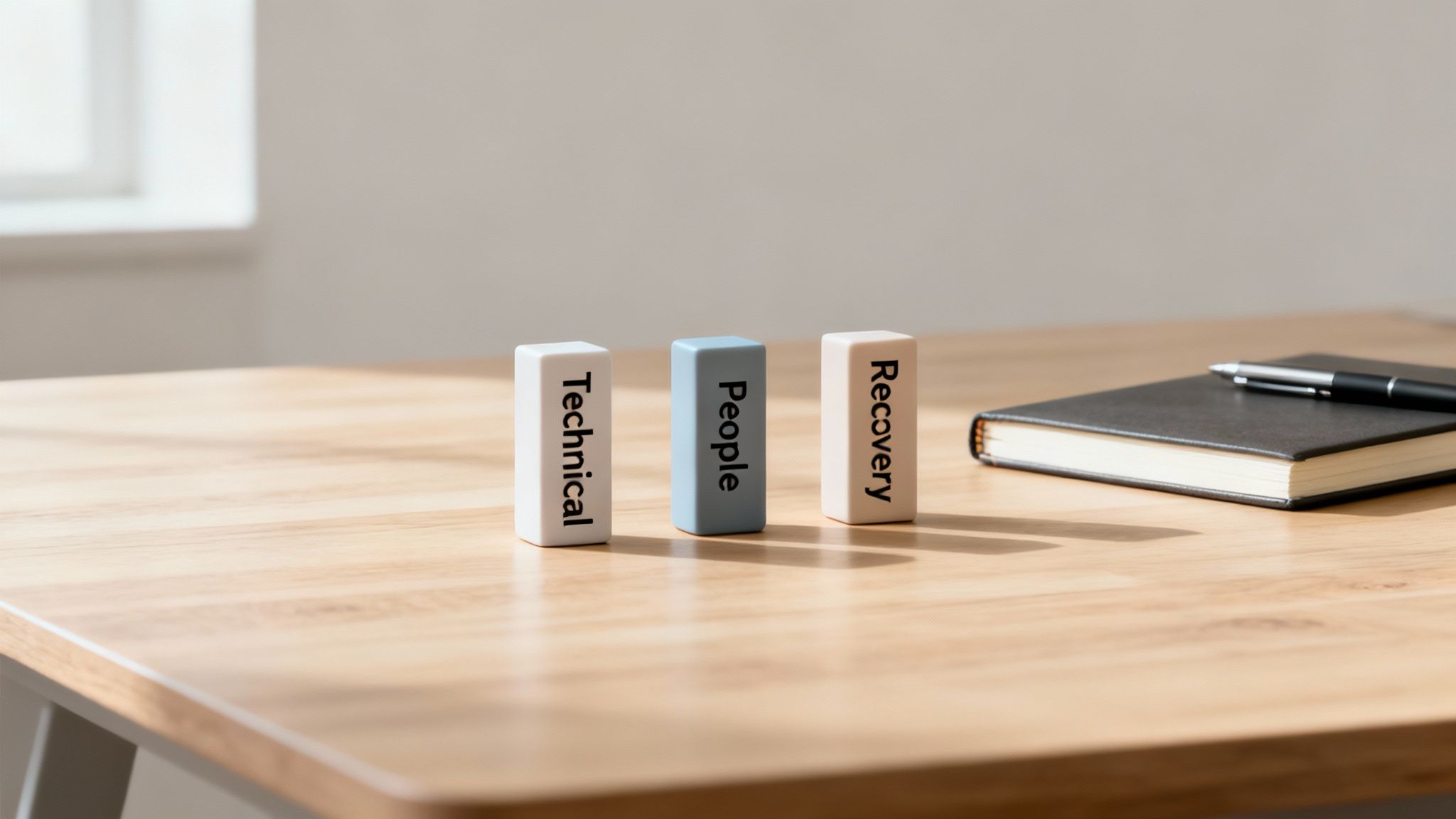
A solid ransomware prevention strategy really comes down to three core pillars. Each one shores up a different part of your security, and together, they create a defense that’s far stronger than any single component.
The Three Pillars of Ransomware Defense
-
Fortifying Your Technical Defenses: This is all about hardening your digital perimeter—your network and your devices. Think properly configured firewalls, advanced email filtering that actually catches sophisticated threats, and modern endpoint security that does more than just scan for known viruses. The whole point is to shrink your "attack surface," effectively locking and barring windows that attackers might try to crawl through.
-
Empowering Your People: Your employees aren't a liability; they're your first line of defense. With the right security awareness training, they can become a human firewall, spotting and reporting the phishing emails, suspicious links, and clever social engineering ploys that technology can sometimes miss.
-
Building a Resilient Recovery Plan: Let's be realistic—sometimes, an attacker might slip through. When that happens, your ability to get back up and running without paying a dime is what matters. This pillar is all about creating a truly reliable backup strategy, one that includes offline and immutable copies of your data that ransomware can't touch.
A layered defense means that if one control fails, another is right there to catch the threat. It’s the difference between having a single chain-link fence and a fortress with a moat, high walls, and lookouts.
To get started, here’s a quick overview of how these pillars work together.
Core Ransomware Prevention Pillars at a Glance
| Pillar | Key Actions | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Defenses | Implement firewalls, endpoint protection, email filtering, and regular vulnerability scanning. | To block malicious software and unauthorized access at the perimeter. |
| Human Firewall | Conduct ongoing security awareness training, run phishing simulations, and establish clear reporting protocols. | To empower employees to recognize and report threats before they escalate. |
| Resilient Recovery | Maintain regular, tested backups with offline/immutable copies and have a documented incident response plan. | To ensure rapid data recovery and business continuity without paying a ransom. |
Each element is critical. Strong tech with untrained users is a recipe for disaster, just as great training with no backups leaves you exposed if a mistake happens.
Understanding the Most Common Ways In
To build a solid defense, you first need to know what you're up against. The vast majority of ransomware incidents don't start with some super-sophisticated, movie-style hack. They begin with simple, common methods that attackers use because, frankly, they work.
Two of the most common ways attackers get a foothold are through phishing emails and exposed Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) ports. Phishing cons an employee into clicking a bad link or opening a weaponized attachment. Unsecured RDP, on the other hand, is like leaving the front door to your network wide open for attackers to walk right in.
The threat isn't just theoretical; it's massive. In 2023, a staggering 59% of organizations worldwide reported being hit by ransomware. That breaks down to an average of 4,000 attacks every single day. The United States was the hardest-hit country, accounting for 47% of all incidents. These aren't just numbers; they're a clear signal for why a proactive defense is non-negotiable, and you can explore more of these ransomware trends from industry analysis. This is the reality we're building our framework to combat.
Hardening Your Technical Defenses Against Intrusions

It all comes down to practical controls that actually disrupt an attacker’s path. Theory is great, but real security means configuring tools so your network feels like a fortress.
Every misconfigured firewall or unpatched server widens your attack surface. Close these gaps one by one and you turn potential entry points into dead ends.
Fortify Your Digital Front Door
Your email gateways and perimeter defenses are usually where ransomware first pokes its head in. Locking them down isn’t optional—it’s the bare minimum.
- Advanced Email Filtering: Beyond spam detection, it inspects links and attachments for hidden malware.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): Watches network behavior in real time, stopping strange traffic patterns before damage occurs.
Imagine swapping a simple lock for a heavy-duty deadbolt, surveillance cameras, and a reinforced frame. That’s what layered defenses feel like to an intruder.
The Unblinking Eye Of Vulnerability Management
Attackers hunt for known flaws—those patches vendors have already released. If you delay updates, you’re leaving a welcome mat out.
- Scanning Frequency: Critical systems should be scanned weekly or even daily, while less vital devices can follow a monthly schedule.
- Patch Deployment: Apply critical updates immediately after testing. Research shows a poor patch cadence can raise ransomware risk by nearly sevenfold.
Staying on top of patches means you’re closing the very windows hackers try to slip through. For deeper insights, check out our guide on network security best practices.
Evolve Your Endpoint Security
Traditional antivirus relied on signature matching, but modern threats morph too quickly. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) brings behavior analysis into play.

An EDR agent monitors process activity and flags anomalies on laptops and servers. That means spotting ransomware as it unfolds, not after files are already encrypted.
By 2025, cybercrime losses—including ransomware—are expected to hit $10.5 trillion worldwide. That’s $333,000 every minute and over 161 billion blocked threats in 2023 alone.
Hardening your defenses is a continuous effort. Advanced filtering, rigorous patch management, and modern endpoint solutions together form a layered shield that keeps intruders at bay.
Building a Human Firewall Through Effective Security Training

All the best firewalls and antivirus software in the world can't protect you from a single, well-intentioned click on a malicious link. The tough reality is that most ransomware attacks don't start with a sophisticated hack; they begin with a simple human error.
This is exactly why your team needs to be more than just users—they need to be your first and most active line of defense. When armed with the right knowledge, your people transform from a potential risk into a powerful "human firewall." Good security training isn't about pointing fingers; it's about building a culture of security awareness where everyone knows the role they play.
Shift from Annual Check-ins to Continuous Learning
Let's be honest: that once-a-year, hour-long security slideshow is a waste of time. Threats change by the day, so your team’s education has to keep up. A continuous learning model is the only way to keep security front and center.
This means ditching the boring presentations for training that actually sticks. Think short video modules, quick interactive quizzes, and scenarios that mirror the real emails and situations your team faces daily. The goal is to make security an instinct, not an annual chore.
Security awareness training is most effective when it’s an ongoing conversation. A single session is quickly forgotten, but consistent reinforcement builds lasting vigilance and turns passive employees into proactive defenders.
By weaving training into the regular workflow, you build muscle memory. Your team starts to instinctively second-guess suspicious emails and pause before clicking unknown links. That moment of hesitation is often all it takes to shut down an attack before it even starts.
Make Phishing Simulations a Positive Learning Tool
One of the most effective ways to train is through phishing simulations. These are controlled, fake phishing emails sent to your team to see how they react in a safe environment. The key here is to frame it as a learning opportunity, not a "gotcha" test.
When someone clicks a simulated phishing link, the response shouldn't be punitive. It should immediately launch a bite-sized training module showing them exactly what red flags they missed.
Here’s what to train your team to spot in a convincing phishing attempt:
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Phrases like "Urgent Action Required" or "Your Account Will Be Suspended" are designed to create panic and bypass critical thinking.
- Suspicious Sender Address: Attackers often use email addresses that are one character off from a legitimate one. Think
dave@gtcornputing.cominstead ofdave@gtcomputing.com. - Unusual Requests: Be wary of emails asking for passwords, financial details, or sudden instructions to change payment information.
- Generic Greetings: A legitimate company will almost always use your name. A generic "Dear Valued Customer" is a major red flag.
Running these simulations regularly turns abstract knowledge into a practical, real-world skill for identifying threats.
Establish Simple and Clear Security Policies
Training is only half the battle. It needs the support of clear, simple, and easy-to-follow policies. If your security manual is a 50-page document filled with technical jargon, nobody is going to read it.
A strong password policy is a great place to start. It’s fundamental to stopping credential theft, which is often the first step in a ransomware attack. You can get a deeper look at this in our guide on password security best practices.
Beyond passwords, your policies should clearly cover:
- Data Handling: Define what is considered sensitive data and set clear rules for how to store, share, and ultimately dispose of it.
- Acceptable Use: Outline the proper use of company devices and networks, especially rules about installing unauthorized software.
- Incident Reporting: Create a simple, no-blame process for employees to report anything suspicious. Make it known that it's always better to report a potential issue, even if it turns out to be nothing.
When your team is well-trained and backed by straightforward policies, they become a truly formidable defense. They’re empowered not just to protect themselves, but to actively protect the entire organization from a devastating attack.
Your Last Line of Defense: A Bulletproof Data Backup and Recovery Strategy
Let’s be honest. Even with the best defenses, a determined attacker might find a way through. When that happens, your backups are all that stand between a minor inconvenience and a full-blown catastrophe. A backup is one thing, but a proven, reliable recovery strategy is what truly makes your business resilient.
This isn't about just dragging and dropping files to an external drive. It's about building a system so robust that you can restore your operations quickly and completely, making any ransom demand totally irrelevant. Think of it as your ultimate safety net, one that completely removes the attacker's leverage.
The 3-2-1 Rule: Your Foundation for Resilience
In the world of data protection, the 3-2-1 rule is the gold standard. It’s a simple, powerful framework for building redundancy and ensuring you always have a clean copy of your data, no matter what happens.
Here’s how it works:
- Three Copies of Your Data: You need your live, production data plus two additional backups.
- Two Different Media Types: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Store your backups on at least two separate forms of media, like a local Network Attached Storage (NAS) device and a cloud service.
- One Copy Off-Site: This is critical. At least one of those backup copies has to live in a completely different physical location. This is your protection against a fire, flood, or theft at your primary site.
Following this simple rule means a single event can't wipe you out. If ransomware hits your server and infects your locally-attached backup, that off-site copy remains untouched and ready to save the day.
Why Immutable and Offline Backups are Non-Negotiable
Modern ransomware is nasty. It doesn't just encrypt your live files; it actively hunts down and destroys your backups to leave you with no choice but to pay. This is precisely why immutable backups have become such a game-changer.
An immutable backup is exactly what it sounds like—once it's created, it can't be changed or deleted for a specific period. It’s a "write-once, read-many" copy that is completely walled off from any malicious process. Many cloud providers offer this, and it's a feature worth paying for.
An offline, or "air-gapped," backup takes this a step further by being physically disconnected from the network. Because there's no live connection, ransomware simply cannot reach it. This is your absolute final fallback if every other digital copy gets compromised.
The goal here is simple: have at least one copy of your data that is completely out of reach. If you're looking for professional help implementing these advanced strategies, you can learn more about specialized data backup services.
Before deciding on a backup solution, it's important to understand the trade-offs between keeping your data on-site versus in the cloud. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses when it comes to security, cost, and accessibility.
Comparing On-Premise vs Cloud Backup Solutions
| Feature | On-Premise Backups | Cloud-Based Backups |
|---|---|---|
| Control & Ownership | Full physical control over hardware and data. | Data is stored on third-party servers; you control access. |
| Initial Cost | High upfront cost for hardware (servers, NAS). | Low to no upfront cost; subscription-based (OpEx). |
| Recovery Speed | Very fast for local restores over the LAN. | Can be slower, dependent on internet bandwidth. |
| Scalability | Limited by physical hardware; requires new purchases to expand. | Highly scalable; storage can be increased on demand. |
| Maintenance | You are responsible for all hardware maintenance and updates. | The cloud provider handles all hardware and infrastructure. |
| Off-Site Protection | Requires a separate physical location and logistics to manage. | Inherently off-site, protecting against local disasters. |
Ultimately, many businesses find that a hybrid approach—combining the speed of local backups with the security of an off-site cloud copy—offers the best of both worlds and aligns perfectly with the 3-2-1 rule.
Test Your Restores. Then Test Them Again.
I can't stress this enough: a backup you haven't tested is not a real backup. It's just a hope. Too many businesses find out their backups are corrupted or incomplete only when they’re scrambling to recover from an attack. That’s a nightmare scenario you have to avoid.
Regularly testing your restore process is non-negotiable. At a minimum, you should be doing a full test restore at least once per quarter. For your most mission-critical systems, I recommend testing monthly. This exercise accomplishes two vital things:
- It verifies data integrity. You’ll know for sure your backup files are good and can actually be used.
- It builds procedural muscle memory. Your team will know the exact steps to take, which cuts down on panic and human error during a real crisis.
Document every step of the restore process. Time it. This will help you set a realistic Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and give you the confidence that you can actually meet it when the pressure is on.
Crafting Your Incident Response Plan Before a Crisis
https://www.youtube.com/embed/UYW55gr1WKo
Panic is a terrible business strategy. Yet, for so many organizations hit with ransomware, that's exactly what takes over. Without a clear plan, teams scramble, critical steps get missed, and the damage spirals out of control, going far beyond just a few encrypted files.
An Incident Response (IR) Plan is your pre-written playbook for that worst-day scenario. It's what turns a high-stress, chaotic event into a calm, methodical process. By defining roles, responsibilities, and specific actions before an attack ever happens, you guarantee a coordinated response that drastically minimizes downtime and financial loss.
Defining Key Roles and Responsibilities
The first thing any solid IR plan needs to do is answer the question: who does what? When an incident is detected, you don't have time to debate who has the authority to pull a server offline or who should be drafting the email to your customers.
Get these roles assigned now, and make sure you have backups for each one:
- Incident Commander: This is your point person—the one who leads the entire response, makes the tough calls, and keeps all the teams in sync.
- Technical Lead: They're in the trenches, managing the hands-on technical work. Think forensic analysis, containment, and eventually, system restoration.
- Communications Lead: This person handles all messaging, both internal and external. Their job is to ensure a consistent, accurate flow of information to employees, clients, and maybe even the media.
- Legal/Compliance Liaison: They get legal counsel on the line and make sure you're meeting all your regulatory and legal notification requirements.
Documenting this chain of command clearly is a game-changer. It eliminates confusion and empowers your team to act decisively when every second counts.
The sophistication of modern threats makes this preparation non-negotiable. The hard truth is that attackers often come back. A global survey found that a staggering 78% of organizations reported being targeted by ransomware, with 32% getting hit three or more times. And paying the ransom is no silver bullet—29% had to make multiple payments, and 70% took more than a day just to get back to normal. You can find more real-world data on these ransomware recovery challenges on semperis.com.
The Six Phases of Incident Response
A truly comprehensive IR plan isn't just a single checklist; it follows a structured, multi-phase approach. This framework ensures you cover all your bases, from the moment you suspect something is wrong all the way to long-term improvements.
- Preparation: This is the phase you're in right now. It’s all about crafting the plan, assigning those key roles, and making sure your team has the right tools and training.
- Identification: How will you know an attack is even happening? This phase defines the triggers that kick your plan into gear, like an alert from your EDR system or a sudden spike in unusual file activity.
- Containment: The absolute first priority is to stop the bleeding. This means isolating infected systems from the rest of the network to prevent the ransomware from spreading any further.
- Eradication: Once you've contained the threat, you have to get it out of your environment completely. This isn't just about deleting the malware; it's about eliminating every trace from every affected device.
- Recovery: With the threat gone, you can finally start restoring systems from your clean, tested backups. This is the moment your diligent backup strategy truly pays off.
- Lessons Learned: After the dust settles, it's time for a post-incident review. What went well? What didn't? Use these insights to update your plan and make your defenses even stronger for next time.
Think of an Incident Response plan like a fire drill. You hope you never have to use it, but practicing the steps ensures everyone knows exactly how to get to safety without hesitation when the alarm bells ring.
This infographic drives home the core principle of a resilient recovery strategy—the classic 3-2-1 backup rule—which is a cornerstone of any effective IR plan.
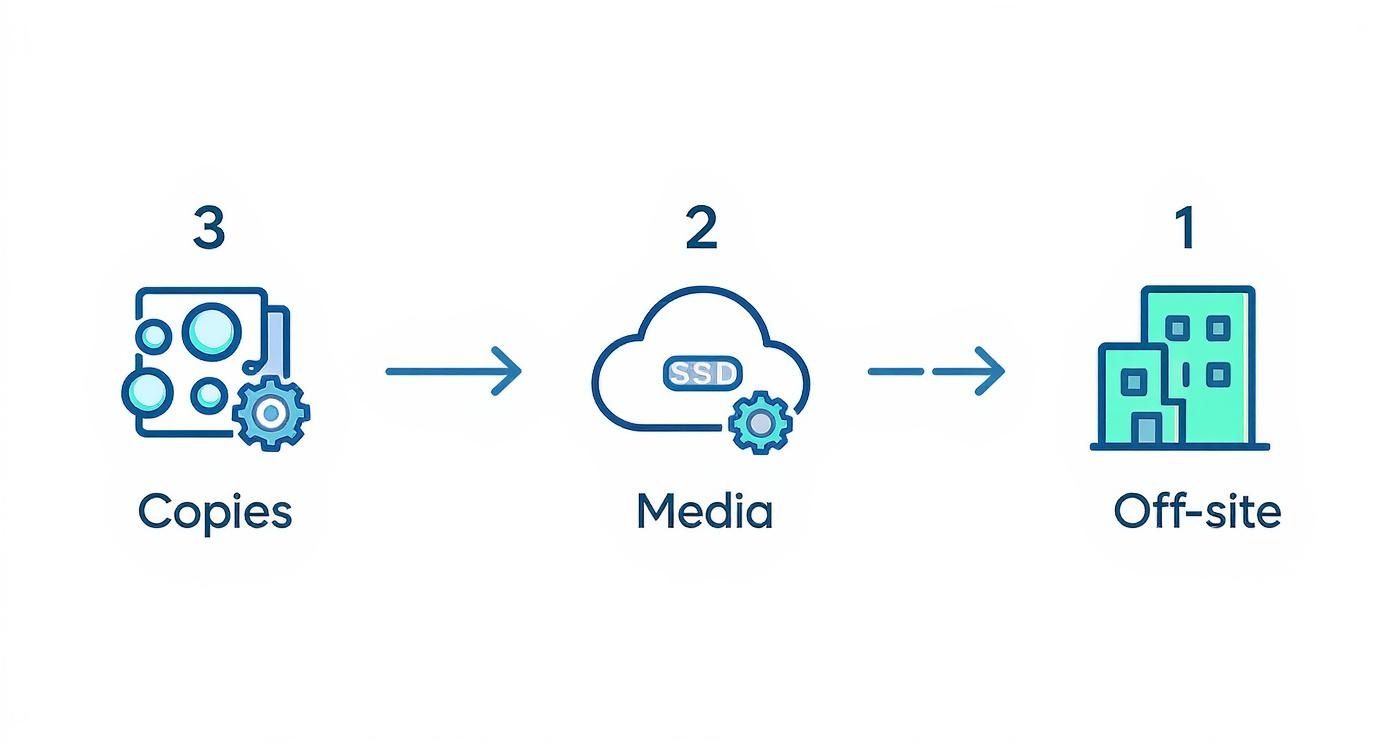
Simply put, having three copies of your data on two different types of media, with one of those copies stored off-site, gives you the redundancy needed to survive a catastrophic event like ransomware.
By mapping out your response in advance, you shift from a reactive state of panic to a proactive state of control. This preparation is the ultimate answer to preventing a ransomware attack from causing irreversible harm to your business.
Your Ransomware Prevention Questions Answered
Is Paying the Ransom Ever a Good Idea
In the heat of a ransomware attack, you might feel the urge to pay just to get back online. Yet experts—and organizations like the FBI—strongly recommend no. There’s zero assurance the criminals will hand over a working decryption key, and too often they don’t.
Sending money also flags your business as a willing target. Once attackers know you’ll pay, they’ll circle back—or even sell your info to others. Plus, every dollar you hand over funds more sophisticated attacks against other victims.
Make the ransom demand irrelevant. A rock-solid backup and recovery plan, tested regularly, strips attackers of any leverage.
How Can a Small Business Implement These Measures On a Budget
Robust cybersecurity needn’t come with a hefty price tag. Many of the most effective controls are free or inexpensive, relying on process and vigilance rather than costly tools. Focus on a few high-impact basics:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Most services include MFA at no extra charge. Enforce it on email, VPNs and essential apps to stop attackers who’ve snagged a password.
- Cost-Effective Cloud Backups: A reliable cloud service satisfies the “off-site” requirement of the 3-2-1 rule without maintaining a second physical location.
- In-House Security Training: No fancy platform needed—review phishing red flags during team meetings, dissect real scam emails and foster a culture where everyone feels safe asking, “Does this look off?”
- Automatic Software Updates: Enable auto-updates for OSes, browsers and applications. This simple, zero-cost step closes the security holes attackers love to exploit.
What Is The Single Most Important Step To Prevent Ransomware
If you could prioritize only one control, it’s a robust, regularly tested backup and recovery plan that includes offline or immutable copies. This is your ultimate safety net.
All other defenses aim to block attackers. A proven backup strategy assumes they’ll break through eventually and gives you a clear path back to business as usual.
How Often Should We Test Backups And Train Staff
Consistency is key. Regular drills and refreshers ensure systems and people stay sharp.
For Staff Training:
- Annual Workshops: Deep-dive into phishing tactics, password hygiene and incident reporting.
- Onboarding Sessions: Instill security habits from day one.
- Monthly Simulations: Send practice phishing emails and debrief immediately to reinforce lessons.
For Backup Testing:
- Quarterly Full Restores: Run a complete recovery of a non-critical system each quarter to validate your process.
- Monthly Spot Checks: Verify mission-critical files or databases to confirm those backups remain intact.
The goal is unwavering confidence that you could bounce back instantly if ransomware struck tomorrow.
Bringing It All Together for a Secure, Productive Business
Building a robust defense against ransomware isn't about a single magic-bullet solution. It’s about weaving together all the pieces—technical controls, employee training, and a rock-solid recovery plan—into the daily fabric of your operations. When these elements work in harmony, you’re not just reacting to threats; you’re proactively dismantling them before they can ever take hold.
Think of it this way: a team that regularly runs through fire drills is far better prepared when a real fire breaks out. The same principle applies here. When your staff has participated in response simulations and understands what a real incident looks like, their instincts take over. They become your first and best line of defense, spotting and reporting suspicious activity before it escalates.
Ultimately, the goal is to keep your business running smoothly, without the constant worry of IT disruptions. At GT Computing, we specialize in providing that peace of mind through fast, reliable support and comprehensive managed IT services.
From setting up secure networks and planning for data recovery to providing 24/7 remote monitoring, we handle the technical heavy lifting so you can stay focused on what you do best.
Ready to build a more resilient business? Let's talk.
Contact us today for a free consultation. Give us a call at 203-804-3053 or email Dave at Dave@gtcomputing.com. You can also learn more on our website: www.gtcomputing.com.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com



