Ever wonder how your team effortlessly shares files, jumps on video calls, or accesses cloud software? The silent hero behind it all is your network infrastructure. Think of it as the digital nervous system of your entire business, the complete framework of hardware, software, and services that makes modern work possible.
Your Business's Digital Nervous System

A great way to picture your network infrastructure is to think of it like a city’s road system. It’s a complex web of physical roads (cables and access points), traffic signals (routers and switches), and addresses that guide information from point A to point B efficiently and safely.
Just as a city would grind to a halt without its roads, a modern business simply can't function without its network. This often-invisible foundation is one of the most critical assets for your company's day-to-day productivity, security, and future growth. It's the backbone supporting every single click, call, and transaction.
What Makes Up a Network Infrastructure?
So, what exactly is included in this "digital nervous system"? It’s a whole lot more than just the Wi-Fi router in the corner. A complete network infrastructure is a symphony of interconnected parts all working together.
To get a clearer picture, let's break down the main components into a few key areas.
Key Elements of Network Infrastructure at a Glance
This table gives a quick overview of the core categories that form a complete network infrastructure.
| Category | Core Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | The physical equipment that creates and connects the network. | Routers, switches, servers, firewalls, wireless access points, cabling. |
| Software | The programs that manage, secure, and monitor the network. | Network operating systems, security software, monitoring tools. |
| Services | The functions that make the network usable and operational. | Internet access, IP addressing (DHCP), domain name system (DNS). |
As you can see, it's a combination of tangible gear, the logic that runs it, and the services that bring it all to life.
The scale of this ecosystem is massive. The global network infrastructure market was valued at an incredible $89.925 billion in 2021 and is on track to hit $105.2 billion by 2025. This explosive growth underscores just how essential these systems are to businesses everywhere. For a deeper dive, you can explore the full market analysis from Cognitive Market Research to see the latest industry trends.
In short, your network infrastructure is the platform that all your IT services are built on. A slow, unreliable, or insecure network will directly cripple your team's ability to get work done and serve customers, which is why its design and management should be a top priority.
Meet the Core Components of Your Network
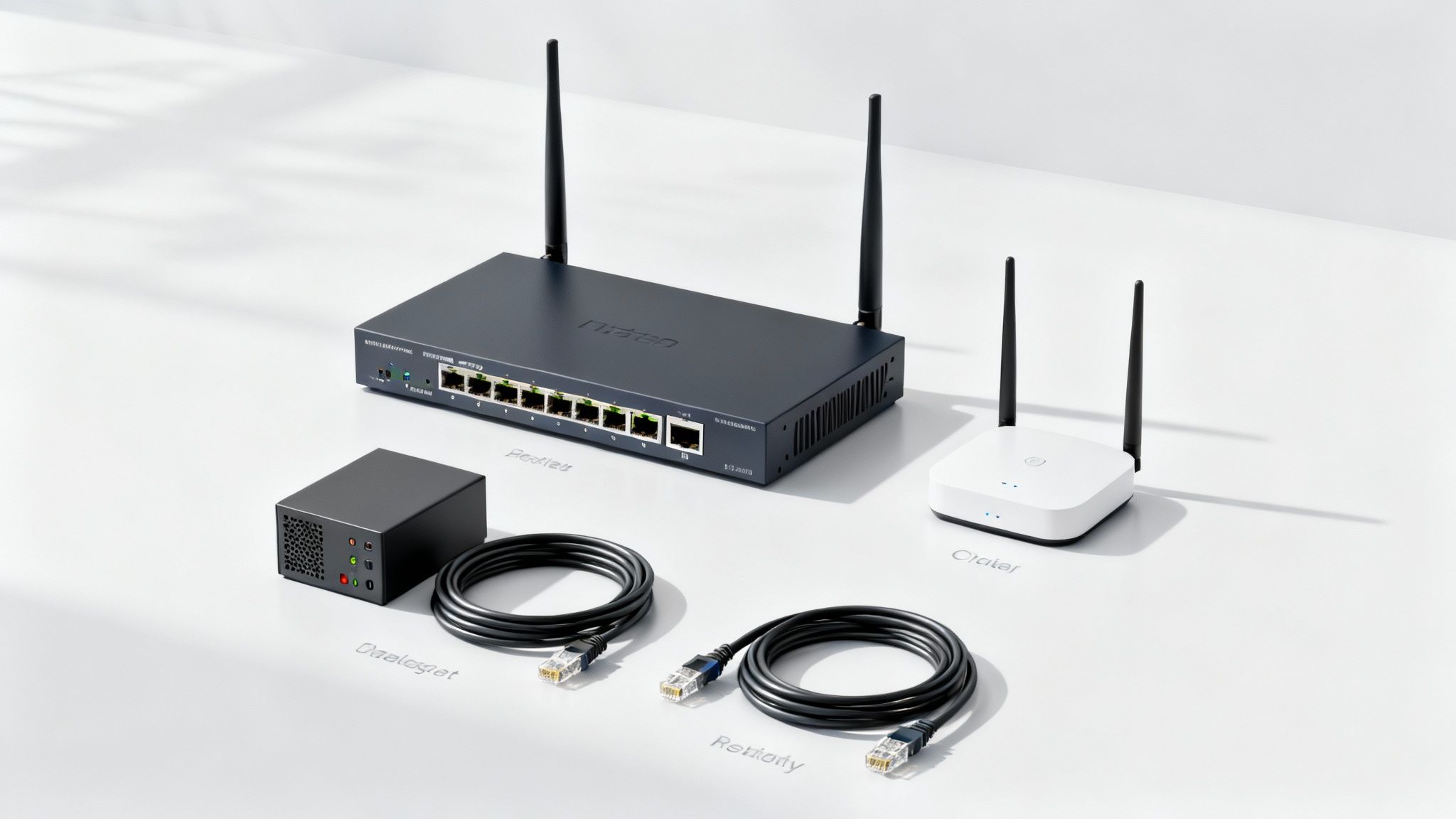

To really get a grip on network infrastructure, we need to pop the hood and look at the essential building blocks. Think of these hardware components as a well-oiled team, where each player has a specific job to keep your digital communication flowing smoothly, securely, and without a hitch.
Let's use a simple analogy: imagine your network is a massive, incredibly efficient logistics company. Every piece of hardware plays a part in getting data "packages" from point A to point B without them getting lost, stolen, or damaged along the way.
The Digital Traffic Directors and Mail Sorters
At the very heart of the operation, you have routers and switches. These two devices are all about managing the flow of information. While they might look similar sitting on a rack, they have very different—but equally important—jobs in directing your data traffic.
Routers are the master traffic controllers of your network. Their main purpose is to connect different networks, most importantly linking your internal business network to the great wide world of the internet. A router looks at a data packet, checks its destination address, and figures out the most efficient route for it to travel, whether that's to the desk across the office or a server on the other side of the planet.
Switches, on the other hand, act more like the internal mail sorters for your building. A switch is what actually creates your local network, connecting all the devices in one physical location—computers, printers, servers, you name it. When someone sends a document to the office printer, the switch makes sure that data packet goes directly to the printer, not to every other computer on the network.
These two components form the core of your connectivity. The switch handles all the local, internal chatter, while the router is your gateway to the outside world.
The Gatekeepers and Hubs of Your Network
Beyond just directing traffic, your infrastructure needs to be protected and accessible. This is where firewalls and wireless access points come in. They act as the security guards and public squares of your digital environment.
-
Firewalls are the vigilant security guards posted at the very edge of your network. Their job is to monitor every bit of incoming and outgoing traffic, checking data packets against a strict set of security rules. A firewall is what blocks malicious traffic, stops unauthorized access attempts, and deflects other cyber threats before they can cause any real damage.
-
Wireless Access Points (WAPs) are the devices that blanket your office in Wi-Fi. They physically connect to your wired network with a cable and then broadcast a wireless signal. This is what allows laptops, smartphones, and other gadgets to connect to the network without being tethered by a cord. In most businesses, you'll see multiple WAPs strategically placed to ensure strong, seamless coverage everywhere from the conference room to the break room.
The Foundation and Central Library
Finally, we have the components that provide the physical pathways and the central storage for all this digital activity. We're talking about the cables that carry the data and the servers that hold and manage it.
Cabling is the literal nervous system of your network. Those ethernet cables snaking through the walls and ceilings are the highways that data travels on between switches, routers, computers, and servers. The quality and organization of this wiring, known as structured cabling, has a massive impact on your network's speed and reliability. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on what is structured cabling.
Servers are your network's centralized data libraries. These are powerful, purpose-built computers designed to store, process, and manage network data and systems 24/7. Whether it's hosting your company website, running your email system, or storing shared files, servers do all the heavy lifting behind the scenes to provide the resources your team and customers rely on.
The Business Impact of a Solid Network Infrastructure
It’s one thing to know what all the pieces of a network are, but it’s another thing entirely to see how they actually make your business run. A well-built network isn't just an IT line item on your budget; it’s the engine quietly powering every single tool, app, and process your team depends on every day.
Just think about it. Your cloud accounting software, the VoIP system you use for crystal-clear client calls, the collaboration tools that keep your remote team in sync—they all rely on a fast, stable network connection. When that connection falters, those critical tools grind to a halt, and your bottom line feels the impact almost immediately.
Fueling Productivity and Collaboration
A solid network is a massive force multiplier for your team's productivity. When employees can pull up shared files in an instant, hop on a video call without that dreaded lag, and use cloud apps without a hitch, they can actually focus on their work instead of fighting with technology. That efficiency isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a real competitive edge.
This reliability is the foundation for almost everything a modern business does:
- Seamless Communication: Keeping VoIP calls and video meetings clear, crisp, and professional.
- Rapid Data Access: Letting your team grab files from a server or the cloud without waiting.
- Stable Application Performance: Making sure your CRM, project management tools, and other essential software just work.
A slow or spotty network doesn't just cause big outages. It creates a death-by-a-thousand-cuts scenario, where tiny, constant interruptions add up to a huge amount of lost time and focus. A strong network gets rid of those digital speed bumps.
Enabling Growth and Scalability
As your business expands, your network has to be ready to keep up. A scalable infrastructure means you can bring on new team members, open another office, or roll out new software without having to rip everything out and start from scratch. That kind of agility is what lets you jump on new opportunities as they appear.
The demand for fast, reliable connectivity is absolutely exploding. The market just for the service provider network infrastructure—the backbone that supports our internet and telecom providers—is valued at a staggering $159.68 billion in 2025. It’s expected to hit $233.44 billion by 2034. That massive investment, fueled by things like 5G and cloud services, shows just how critical this digital foundation has become for businesses like yours. You can dig deeper into these trends in the service provider network market.
To keep things running smoothly as you grow, you can't just set it and forget it. Using the best network monitoring tools helps you stay ahead of problems, track performance, and make sure your network can handle whatever you throw at it. A healthy network isn't just about keeping the lights on today; it's about paving a smooth road for where your company is headed tomorrow.
Choosing Your Infrastructure: On-Premise, Cloud, or Hybrid?
Once you have a handle on the components that make up a network, the next big question is a practical one: where is all this technology actually going to live? This isn't just a technical detail; it's a major strategic decision that will shape your budget, your team's responsibilities, and how quickly your business can adapt to change.
Essentially, you have three primary paths to choose from. Each model—on-premise, cloud, and hybrid—comes with its own unique set of pros and cons. The right choice for you will come down to a careful balance of what your business needs most, whether that's total control, maximum flexibility, ironclad security, or predictable costs.
On-Premise Infrastructure: The Traditional Approach
Running your infrastructure on-premise is the classic model. Think of it like owning your own commercial building. You buy, house, and maintain all the physical hardware yourself—every server, switch, and firewall sits in your office or a dedicated server room.
This path gives you ultimate, granular control over your entire network and every piece of data. The flip side? You're also on the hook for everything. That includes the hefty upfront investment in equipment, plus all the ongoing costs for power, cooling, maintenance, security patches, and eventual hardware upgrades.
Cloud Infrastructure: The Modern, Flexible Route
In complete contrast, cloud infrastructure is more like leasing a state-of-the-art office space in a fully serviced building. Instead of buying your own servers, you're essentially renting computing power, storage, and networking services from a major provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
This model flips the financial script, swapping large capital expenditures for a more predictable monthly operational cost. The major draws here are incredible scalability—you can add more resources with a few clicks—and the fact that the cloud provider handles all the tough hardware management and physical security. The market reflects this shift; in the first quarter of 2025 alone, global spending on cloud services soared to $90.9 billion, a 21% jump from the previous year. You can dig into the full details in the latest report on trends in global cloud infrastructure spending.
Hybrid Infrastructure: The Best of Both Worlds
So, what if you want the control of owning your building but the flexibility of a lease? That’s where hybrid infrastructure comes in. This approach is a strategic blend of the on-premise and cloud models, allowing you to mix and match. For instance, you could keep your most sensitive customer data on private servers you own and control, while using the public cloud for your website, development environments, or to handle unexpected surges in demand.
This model offers a powerful balance, letting you maintain tight control over core assets while still tapping into the cloud's fantastic scalability and cost-efficiency. It’s the go-to solution for businesses with complex or evolving needs.
Comparing Network Infrastructure Models: On-Premise vs. Cloud vs. Hybrid
Making the right call requires a clear look at the trade-offs. This table breaks down how each model stacks up against the key factors that matter most to business owners.
| Factor | On-Premise | Cloud | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | High upfront capital expense (CapEx) for hardware; ongoing operational costs for maintenance, power, and staff. | Operational expense (OpEx) model with pay-as-you-go pricing; no upfront hardware costs. | A mix of CapEx and OpEx; can be complex to manage but offers cost optimization opportunities. |
| Control & Customization | Complete control over hardware, software, and security configurations. Highly customizable to specific needs. | Limited to the provider's offerings and configurations. Less granular control over the physical infrastructure. | High control over on-premise components, combined with the provider-managed environment of the cloud. |
| Scalability | Limited and slow to scale. Requires purchasing and provisioning new physical hardware. | Highly scalable and elastic. Resources can be scaled up or down in minutes to meet demand. | Excellent scalability by "bursting" into the cloud to handle peak loads while keeping a stable on-premise baseline. |
| Security & Compliance | Full responsibility for physical and network security, as well as meeting compliance standards. | Shared responsibility model. The provider secures the infrastructure, while you secure your data and applications. | Complex security management, as you must secure both environments and the connections between them. |
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your unique business goals, budget, and technical expertise. A startup might lean toward the cloud for its low entry cost, while a financial firm might prefer an on-premise or hybrid model for maximum data control.
As the graphic above shows, no matter which model you land on, a well-designed network is the foundation for everything else. It’s what drives productivity, protects your assets, and gives you the room to grow.
Best Practices for a Secure and Reliable Network

Just having a network isn't enough to get the job done. Think of it like a high-performance car—it needs regular tune-ups and a skilled driver to keep it running at its peak. Your network is only as strong as its management, and a few non-negotiable best practices are the key to keeping it secure, reliable, and efficient.
Getting these habits right protects your digital assets, keeps the lights on during a crisis, and turns your network from a potential weak point into a real operational advantage. Ignoring them is like leaving the front door of your business unlocked.
Implement a Layered Security Approach
First things first: build a solid defense. In the face of modern cyber threats, a single lock on the door just won’t cut it. Instead, you need a layered security strategy that creates multiple barriers. The goal is to make your network a much harder, and less appealing, target for attackers to bother with.
This approach combines a few essential tactics to create a truly robust defensive wall:
- Strong Firewalls: This is your network's primary gatekeeper. A well-configured firewall acts like a security guard, inspecting all traffic coming in and out and blocking anything that looks suspicious before it can do any damage.
- Access Controls: This is all about the principle of least privilege. In simple terms, employees should only have access to the specific data and systems they absolutely need to do their jobs. Nothing more.
- Endpoint Protection: Every single device connected to your network—from the main server down to the newest employee's laptop—needs up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software. No exceptions.
Stay Diligent with Updates and Patches
Software vulnerabilities are one of the most common ways attackers sneak into a network. Developers are constantly finding and fixing these security holes by releasing updates and patches, but those fixes are useless until you actually install them.
Procrastinating on software updates is like knowing a window in your office is broken but waiting to fix it. It’s an open invitation for trouble. Regularly updating your operating systems, applications, and firmware is a simple yet powerful way to shrink your attack surface.
Plan for the Unexpected with Backups and Recovery
Sooner or later, downtime happens. It might be a hardware failure, a bad storm, or a cyberattack, but at some point, your systems will likely go offline. A solid data backup and disaster recovery plan is what decides whether this event is a minor hiccup or a full-blown catastrophe.
A good plan always includes:
- Regular, automated backups of all your essential business data.
- Off-site or cloud storage for those backups, so they’re safe from local disasters like a fire or flood.
- A clear recovery procedure that spells out exactly how to get operations back up and running fast.
Building in resiliency is also a huge part of this. For anyone interested in creating systems with built-in fail-safes, you can learn more about what is network redundancy in our detailed guide. It's a foundational strategy for making sure your business stays online even when individual components fail.
Your Network Infrastructure Questions Answered
Even when you've got a handle on the components and the big-picture strategy, questions always pop up in the day-to-day management of your network. Let's tackle some of the most common ones we hear from business owners to help you make smarter, more confident IT decisions.
How Often Should I Upgrade My Network Hardware?
There’s no magic number that fits everyone, but a good rule of thumb is to take a hard look at your core network gear—your routers, switches, and firewalls—every 3 to 5 years. The right time to upgrade really boils down to three things: performance, security, and your own business needs.
Is your team constantly complaining about sluggish speeds? Has your hardware gotten so old that the manufacturer stopped pushing out critical security updates? If you answered yes to either of those, it's definitely time for an upgrade. Being proactive here helps you get ahead of performance bottlenecks and patch up security holes before anyone can take advantage of them.
What Is the Real Difference Between a Router and a Switch?
This is a classic, and it's a point of confusion for a lot of people. The easiest way to remember the difference is with a simple analogy.
Think of a switch as the internal mail sorter for your office. Its sole job is to connect all the devices inside your building—computers, printers, servers—and make sure a file sent from one desk gets to the right computer down the hall. A router, on the other hand, is like the central post office. It connects your entire office building to the outside world, most importantly connecting your local network to the internet.
So, for any typical business, you absolutely need both. The switch keeps all your internal traffic moving smoothly, while the router acts as the gateway for all communication coming in and going out.
Can My Small Business Afford a Professionally Managed Network?
Yes, absolutely. In fact, for a lot of small businesses, it’s far more cost-effective to outsource IT management than to hire a dedicated, full-time IT person. It's a common misconception that professional support is a luxury reserved for big corporations.
Managed IT services give you access to an entire team of experts for a predictable, flat monthly fee. This model drastically reduces the risk of getting hit with a massive, unexpected bill when something big goes wrong, like major downtime or a security breach. It’s an investment in stability and peace of mind that often pays for itself by preventing expensive problems before they start.
Building the Backbone of Your Business
Think of your network infrastructure as the central nervous system of your entire business. It's the invisible force that powers every single digital action, from the simple act of sending an email to running sophisticated cloud-based software. Every click, every customer call, and every transaction relies on this digital backbone to function.
This is why a well-designed and secure network isn't just an IT expense—it's one of your most critical business assets.
Investing in a solid network has a direct impact on your company's growth, day-to-day productivity, and overall security. It gives your team the tools to work without constant tech-related slowdowns and provides the stable foundation you need to bring in new technologies and keep your clients happy. Simply put, this system is what allows your business to compete and grow.
A strong, professionally managed network isn't just a utility running in the background; it's a real competitive advantage. It keeps your operations smooth, your data safe, and your company ready for whatever comes next.
At the end of the day, understanding network infrastructure is about recognizing just how central it is to your success. When you make its health and performance a priority, you're directly investing in the long-term stability and potential of your business. A reliable network is the bedrock of modern commerce, giving you the confidence to operate today and the ability to scale tomorrow.
Keep your business running without IT headaches.
GT Computing provides fast, reliable support for both residential and business clients. Whether you need network setup, data recovery, or managed IT services, we help you stay secure and productive.
Contact us today for a free consultation.
Call 203-804-3053 or email Dave@gtcomputing.com



